Protect Your Vision with Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment – A Complete Overview
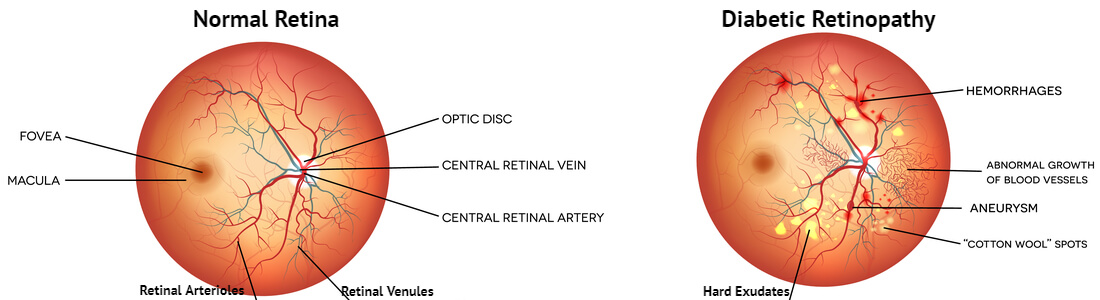
Diabetic Retinopathy is the eye disease that affects the people with diabetes and thus falls under the category of Diabetic Eye Disease. The condition of Diabetic Retinopathy can develop in any diabetic patient who has type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes. During Diabetic Retinopathy, the blood vessels of the retina, a light-sensitive layer of tissue located at the back of the eye, get damaged. At the early stages of the condition, there are no symptoms or only a few mild vision problems occur but when it becomes advanced then it may cause permanent vision loss. A less controlled blood sugar level is the main cause of Diabetic Retinopathy. Therefore, there are preventive measures that you can take to get yourself protected and there are also treatments for Diabetic Retinopathy available that along with early diagnosis can slow down or even stop the progress of the disease.
Here’s what you need to know about Diabetic Retinopathy symptoms, types, causes, risk factors, complications, diagnosis, and treatment:
What are the symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy?
The patient doesn’t notice any symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy in the early stages but they start to appear when the disease becomes severe. These symptoms include:
- Blurry, fluctuating vision
- Impaired color vision
- Black spots or empty areas in vision
- Spots or dark floaters in vision
- Loss of central vision especially when you read or drive
- Vision loss
As the condition affects both the eyes so a patient may experiences these symptoms in both eyes. When you start noticing any of these symptoms then consult the eye doctor immediately.
What are the types of Diabetic Retinopathy and what causes them?
The high blood sugar levels for long period of time block the small blood vessels that nourish the retina, which is a tissue layer at the back of the eye transforming light into the images and keep it healthy. As a result, the blood supply cuts off and the eye starts growing new blood vessels but these new blood vessels don’t develop properly and they weaken and easily leak fluid and blood into the retina.
The condition of Diabetic Retinopathy has two types:
-
Early Diabetic Retinopathy:
This type also called as non-proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR), is a common condition in which new blood vessels are not developing properly. In NPDR, tiny bulges extend beyond the walls of the small blood vessels while leaking blood and fluid in the retina. The large blood vessels inside retina become dilated and due to leakage, the nerve fibers in the retina swell and even the central part of the retina (macula) also swells (a condition, called as Macular Edema). As more and more blood vessels block and new ones develop improperly, the NPDR may progress from mild to severe.
-
Advanced Diabetic Retinopathy:
This is more advanced and severe type, also called as proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR). As the condition progresses and gets worse, more and more blood vessels get blocked that causes the growth of more new and abnormal blood vessels. These all blood vessels can even cause leakage of blood and fluid in the vitreous that is a jelly-like substance filling up the center of the eye. Ultimately, a scar tissue builds up due to the growth of a large number of new blood vessels in the eye and this causes the retina to detach from the back of the eye. If a new blood vessel interferes with the normal flow of fluid out from the eye then a pressure builds up in the eyeball and this damages the optic nerve of the eye (carries images from eye to brain) resulting in developing another eye condition called as Glaucoma.
What are the risk factors of Diabetic Retinopathy?
A person who has diabetes can develop the condition of Diabetic Retinopathy. Moreover, the risk of developing the condition increases if a person has these factors that include having diabetes for a long duration of time, having blood sugar level poorly controlled, have high cholesterol and blood pressure, too much tobacco use and being pregnant.
What are the possible complications of Diabetic Retinopathy?
The complications can lead to some serious vision problems that include vitreous hemorrhage (a condition when too much bleeding from new blood vessels fills up the vitreous cavity and blocks the vision), retinal detachment, and glaucoma and ultimately these complications can lead to permanent vision loss.
How is Diabetic Retinopathy diagnosed?
At first, the eye doctor performs dilated eye exam and during this exam, drops are placed in the eyes to widen the pupils that allow the doctor to have a better view inside the eyes. During this exam, the ophthalmologist looks for the growth of new abnormal blood vessels, scar tissue, swelling and bleeding inside the retina, retinal detachment and any abnormality in the optic nerve.
The ophthalmologist also tests your vision, measure the eye pressure for the presence of glaucoma and looks for any evidence of cataracts.
The eye doctor also performs some other tests which include:
Fluorescein Angiography: The ophthalmologist takes the pictures of the inside of the eyes when they are dilated. After that, he/she injects a dye into the patient’s arm and takes more pictures as the dye circulates through the eyes. These pictures are used to identify those blood vessels that are blocked, destroyed or leaking any fluid.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): It is imaging test that provides the cross-sectional images of the retina and shows the thickness of the retina. The images help in determining whether fluid has leaked into the retinal tissue.
How is Diabetic Retinopathy treated?
The treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy depends on the type and severity of the condition and it is aimed to slow down or stop the progress of the disease.
Treatment for early Diabetic Retinopathy:
If the patient has mild or moderate Diabetic Retinopathy or NPDR then there is no need of treatment at this stage. But, the ophthalmologist monitors the eyes to determine when the patient needs treatment. Meanwhile, the patient should works with the diabetes doctor for managing diabetes because controlled blood sugar levels can slow down the progression of the disease.
Treatment for advanced Diabetic Retinopathy:
If a patient has advanced Diabetic Retinopathy or PDR then surgical treatment is needed promptly. Various surgical procedures can be performed depending on the specific problem with the retina and these surgical options include:
Focal Laser Treatment: It is laser treatment that also refers as photocoagulation and it can slow or stop the leakage of fluid or blood in the eye. The procedure is usually performed in a single session in the eye clinic or doctor’s office and it involves treating the leaks from abnormal blood vessels with the laser burns.
Scatter Laser Treatment: This procedure is also called as pan-retinal photocoagulation in which the abnormal blood vessels shrink with the help of a laser. During the procedure, the areas of the retina that are away from the macula are treated with scattered laser burns that shrink the abnormal blood vessels causing them to form a scar. The patient may get blur vision for one day after the procedure. The procedure is usually performed in two or more sessions in an eye clinic or doctor’s office.
Vitrectomy: This surgical procedure is performed in hospital or surgery center using general or local anesthesia. During the procedure, a very tiny incision is made in the eye and the blood along with scar tissue is removed from the middle of the eye or vitreous.
Remember that regular eye exams and checkups and a good control of blood sugar level or effective diabetes management are the key measures that you can easily take to prevent from Diabetic Retinopathy. Secondly, the early detection and a proper treatment help in slow or stop the progress of the disease thus preventing permanent vision loss.
For effective treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy, contact ophthalmologists at Menger Eye Centers in Glendale, NYC:
If you are experiencing symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy or any other vision problems then you can consult board-certified ophthalmologists at Menger Eye Centers. They are highly recommended in providing the best treatment for Diabetic Retinopathy in NYC and other various eye diseases effectively and efficiently with advanced diagnostic exams and workable customized treatment plan.