How Macular Degeneration Treatment Improves Vision in Older Adults?
A common eye disorder in which a person losses his/her central vision (it is what you see when you look at something straight ahead) is called as Macular Degeneration. The condition of Macular Degeneration occurs when the small central portion of the retina called as “Macula” deteriorates, which controls the sharpness of your vision. The retina is a light-sensitive tissue layer located at back of the eye. Our ability to read, drive, recognize faces, watching TV, using computer and all the other visual tasks that requires us to see every fine detail; all depends on the health of the macula. If macula becomes weaken then this highly affects the sharpness of the vision and we are unable to perform our routine activities.
As the condition of Macular Degeneration develops in older adults, it is also called as Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD or ARMD). Macular Degeneration is the leading cause of vision loss in older adults over the age of 60 years and most common eye condition among American elderly that causes severe vision loss. The condition significantly causes visual disability but early detection, appropriate Macular Degeneration Treatment plan and self-care measures can slow down the progression of vision loss or blindness.
Let’s see the types, signs and symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnosis and treatment of Age-Related Macular Degeneration.
What are the types of Macular Degeneration?
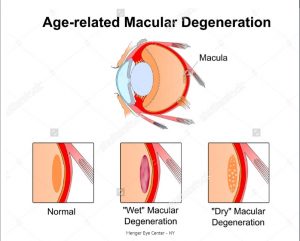
The two main types of Age-Related Macular Degeneration are:
Dry Macular Degeneration:
It is the most common type of AMD that affects around 80-90 percent of people who have AMD. This type of condition occurs when small yellow deposits called drusen develop in the macula. Few small drusen don’t cause changes in vision but when they increase in size and number, they cause dimming or distortion of the vision that commonly occurs during reading. In the advanced stages of dry AMD, the light-sensitive layer of cells in macula becomes thin which leads to tissue death and causes blind spots in central vision and the patient loses central vision.
Wet Macular Degeneration:
It is a rare type of AMD that affects 10-15 percent of people having AMD. This type of condition occurs when abnormal blood vessels grow underneath the macula and they leak blood and fluid into the retina which cause distortion of the vision when straight lines look wavy, blind spots starts appearing and central vision is lost. The bleeding may form a scar which leads to permanent central vision loss.
The dry form of Macular Degeneration can also lead to wet form of the disease, so it is necessary for those who have AMD to monitor their eyesight carefully and see the ophthalmologist regularly.
What are the signs and symptoms of Macular Degeneration?
Macular Degeneration is a progressive condition that means it becomes worse with the passage of time. That is the reason; a patient doesn’t notice any symptoms at the early stages of the disease.
Symptoms of dry Macular Degeneration are:
- Reduced central vision
- Distortion of straight lines in field of vision
- Blurred vision
- Difficulty in doing activities in low lights
- Need brighter light to do activities
- Trouble in recognizing faces
Some of the symptoms of wet Macular Degeneration are same as dry Macular Degeneration such as reduced central vision and visual distortions. Some other symptoms of wet AMD are:
- A dark blurry spot in field of vision
- Rapidly worsening symptoms
- Hazy (vague, cloudy) vision
Both the types of Macular Degeneration don’t affect your peripheral (side) vision.
What causes Macular Degeneration? Are there any risk factors of developing the disease?
The exact cause of AMD isn’t yet known, but there are certain risk factors that increase the risk of developing the condition. These include:
- Being older adult, over the age of 60 years
- Heredity
- Smoking
- Obesity
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol level
- Being light skinned
- Having a light eye color
- Side effects of toxic drugs e.g. anti-malarial drugs or anti-psychotic drugs
How is Macular Degeneration diagnosed?
At first, you should have annual eye exam even if you have normal vision and if you experience any changes in your vision then definitely you should consult the ophthalmologist.
The ophthalmologist performs variety of eye tests to diagnose Macular Degeneration. During an eye exam, the eye doctor uses special eye drops to dilate the eyes for checking the back of eyes for the presence of blood, fluid or yellow deposits. The eye doctor can also performs test to check your field of central vision by asking you to look at a grid, if some of lines appear faded or broken then it can be a sign of AMD. Some other tests for AMD include:
Fluorescein Angiography: In this test, the ophthalmologist injects a colored dye into the vein in arm. Then, he/she uses special camera to take photographs of the eye as the dye circulates in blood vessels of retina. These photographs show the exact location and type of new vessels or vessels leaking blood or fluid in macula, if they are formed.
Optical Coherence Tomography: During this test, the ophthalmologist takes cross-sectional images of retina in order to check any swelling, thinning or thickening.
How is Macular Degeneration treated?
There is no cure of Macular Degeneration but the eye doctor devises treatment options that slow down the progress of the disease and prevent severe vision loss.
For dry Macular Degeneration treatment, the ophthalmologist recommends surgery to improve the vision. During the surgery, a telescopic lens is implanted on the eye that magnifies the field of vision.
For wet Macular Degeneration treatment, the eye doctor prescribes eye medication that stops the growth of new blood vessels. Another treatment option is Photodynamic Laser Therapy, in which the eye doctor injects light-sensitive drug into your bloodstream that is absorbed by the abnormal blood vessels and after that the doctor shines cold laser into eye to activate the drug which then damages the abnormal blood vessels. Laser Therapy is also another treatment option, in which high-energy laser beam is used to destroy abnormal blood vessels that actively grow in macula.
Remember, that only regular eye exams, early diagnosis and a proper treatment plan can slow the progress of the disease and minimizes the chances of severe vision loss while improving your vision.
Visit Menger Eye Centers in Glendale, NYC for treatment of Macular Degeneration:
If you are above 60 years of age and experiences difficulty while doing your routine activities such as reading, driving or recognizing faces then you need to consult ophthalmologists at Menger Eye Centers, as they are highly recommended eye specialists for treatment of Macular Degeneration in Glendale, NYC. They use advanced facilities and equipment for diagnostic eye tests and exams, provide safe and quality treatment with regular post-treatment care. They are fully committed to help you in improving your vision through best eye care treatment.